RIRS
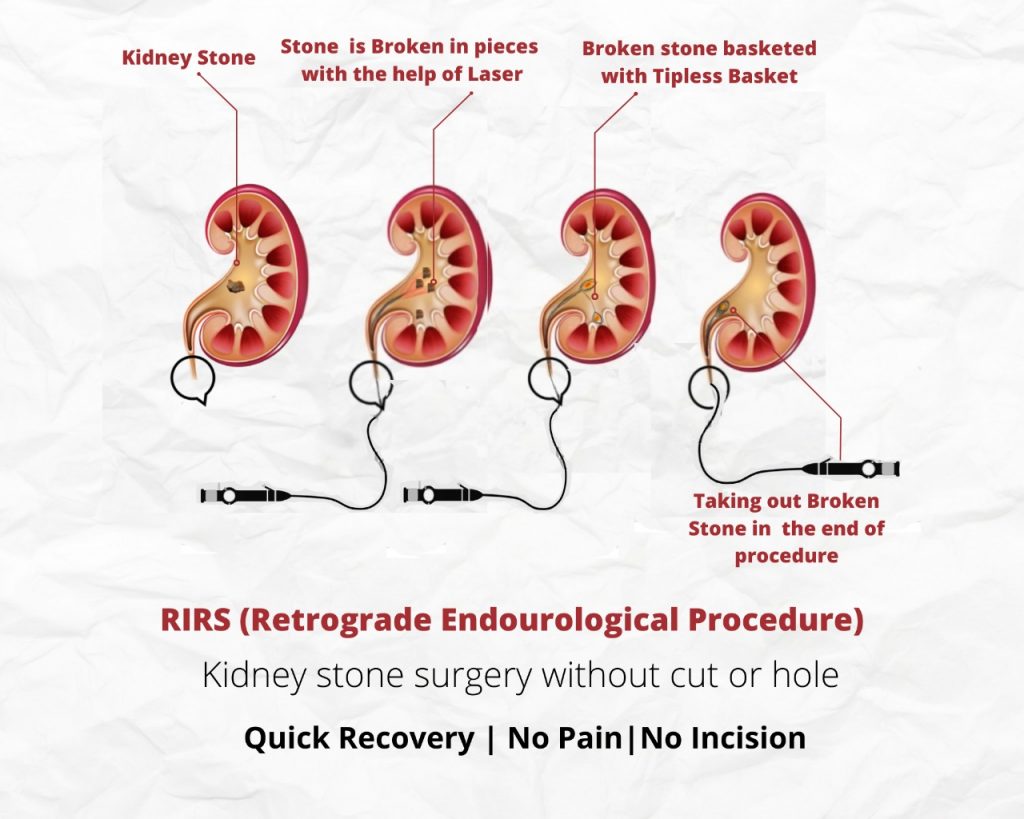
Retrograde intrarenal stone surgery (RIRS) is the most advanced surgery and latest inclusion into the options for kidney stone management. RIRS is performed to remove stones without making any incisions on the kidney while using a laser and a viewing tube called a fiberoptic or flexible ureteroscope that goes through the urethra and reaches into the kidney. It is performed under general or spinal anesthesia. This procedure requires a specialized urologist who is specifically trained in RIRS.
To perform this procedure, the scope is placed through the urethra, into the ureter and finally into the urine-collecting part of the kidney. The scope is therefore moved retrograde, i.e. up the urinary tract system to within the kidney, i.e. intrarenal. Once the scope is in place, it can reach each and every corner of the kidney (usually called as calyces), which is inaccessible during other procedures like PCNL. The doctor can directly see the stone and proceed to manipulate or fragment it by use of laser energy fibers or even grabbed by small-specialized baskets or forceps.
There are several advantages of opting for RIRS over other surgeries like achieving quicker resolution of problems, elimination of prolonged post-surgery pain and a much faster recovery period. It can usually be performed as a day care procedure or may require admission for one day. Majority of kidney stones can be best managed using this modality in the current era except for very large stones or those associated with specific anatomic abnormalities of the kidney. It may be called as the ‘Gold Standard’ treatment for majority of the kidney stones.
RIRS is a minimally invasive urology procedure that is generally used in cases that are otherwise difficult to treat, such as:
- Failed attempts at other treatment modalities
- Solitary or anomalous kidney
- Kidney stones not amenable to lithotripsy or failed lithotripsy
- Strictures in the kidney or ureter
- Tumors in the kidney
- Kidney stones among children
- Bleeding disorders in the kidneys that preclude PCNL or ESWL
- Grossly obese patients
